

Many customers in high-volume online transaction processing (OLTP) environments put their business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) strategy at risk by delaying their regular backup schedules in order to remain operational for customer workloads. While customers use the current compression standard, the challenge many customers have with the current compression implementation is that the compression ratios are frequently too low to justify the additional compute overhead required to compress the backup files.Īdditionally, customers cannot offload the compute overhead of the compression task. The default configuration in SQL Server is to not compress backups, but many users change this default globally using sp_configure. Compressing backup data benefits customers in two ways: first, the backup files will consume less storage, and second, since there are fewer bytes being transferred, the backups run faster than uncompressed backups. Using the metadata in the backup file header, the RESTORE command decompresses compressed backup files. SQL Server backup compression provides the compressed backup option for all streaming SQL Server backup types-full, differential, and transaction log. Processor drivers can help us do just that by overclocking and underclocking the processors.In SQL Server 2008 Enterprise Edition, backup compression was introduced adding WITH COMPRESSION as an option in the T-SQL backup command. However, they are allowed to go beyond the standard settings to provide higher functionalities.

ProcessorsĬPUs generally offer certain performance levels for different processes. Chipset drivers coordinate operations between the motherboard and OS to help the system function to run. The motherboard of the CPU is the central point of operation for most other hardware components connected to it like RAM, graphics card, and more.
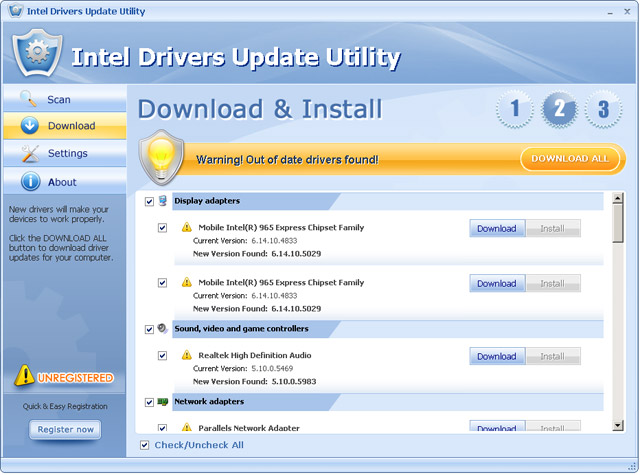
It also enables your PC to communicate with other devices connected to the network system. EthernetĮthernet drivers are necessary for wired LAN connections like optical fiber internet supply, common printers, and scanners. These drivers are used to integrate with wireless network adapters and allow your operating system to connect with WiFi or Bluetooth devices. Wireless drivers are responsible for configuring your hardware with a WLAN cluster and wireless devices like WiFi.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
